Your application may be susceptible to SQL Injection attacks when you incorporate invalidated user input into the database queries. Particularly susceptible is a code that constructs dynamic SQL statements with unfiltered user input.
Consider the following example code:
Sql DataAdapter myCommand = new SqlDataAdapter(
"Select * from Users
Where UserName = ' "+txtuid.Text+" ", conn);
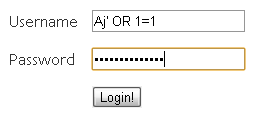
Attackers can inject SQL by terminating the intended SQL statement with the single quote character followed by a semicolon character to begin a new command and then executing the command to their choice. Consider the following character string entered into the .txtuid field.
' OR 1=1
This results in the following statement to be submitted to the database for execution:
SELECT * FROM Users WHERE UserName = ' ' OR 1 = 1;

Because 1=1 is always true, the attacker retrieves very row of data from the user table.
Now, to prevent such an attack, a secure login technique is required. Here, in this article, we discuss the coding of a secure login script using PHP and MySQL.
Step I: Create a database and a table 'members' in it:
CREATE TABLE `members` ( `username` varchar(20), `password` varchar(128) )
Step II: Create a Login Form:
<form action="process_login.php" method="post"> Username: <input type="text" name="username" /><br /> Password: <input type="password" name="password" /><br /> <input type="submit" value="Login" /> </form>
Connect to MySQL Server:
$host = 'localhost'; // Host name Normally 'LocalHost' $user = 'root'; // MySQL login username $pass = ''; // MySQL login password $database = 'test'; // Database name $table = 'members'; // Members name mysql_connect($host, $user, $pass); mysql_select_db($database);
Step III: Now, you need to provide mechanism to avoid SQL Injection. For this, escape special characters like ", ', \
We can escape special characters (prepend backslash) using mysql_real_escape_string or addslashes functions. In most cases PHP will this do automatically for you. But PHP will do so only if the magic_quotes_gpc setting is set to On in the php.ini file.
If the setting is off, we use mysql_real_escape_string function to escape special characters. If you are using PHP version less that 4.3.0, you can use the addslashes function instead.
name = mysql_real_escape_string($_POST['username']);
$password = md5($_POST['password']);
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM $table WHERE username = '$username' AND password = '$password'
");
Here, we use the MD5(Message Digest 5) Algorithm, that generates the message digest for the password. So, while writing the script for registration page, care must be taken that the md5 of the password entered by the user must be stored in the database, instead of the actual text password. In a real world situation, do not use MD5, as it is no longer considered secure. Use some other secure hashing algorithm.
Validating the login:
if(mysql_num_rows($result))
{
// Login
session_start();
$_SESSION['username'] = htmlspecialchars($username);
}
else
{
// Invalid username/password
echo '<p><strong>Error:</strong> Invalid username or password.</p>';
}
// Redirect
header('Location: http://www.example.com/loggedin.php');
exit;